testicular torsion test name|testicular torsion prognosis : bulk Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .
WEBPlay chess online for free on Chess.com with over 150 million members from around the world. Have fun playing with friends or challenging the computer!
{plog:ftitle_list}
Sorvete 250ML quantidade. Comprar. Produtos
Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or . Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding.
Testicular torsion is the twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. It is a urological emergency requiring urgent surgical intervention . It can either be due to an intravaginal (‘bell-clapper deformity’) or extravaginal cause.
moisture meter for plastic granules
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of. Ultrasound is a sensitive and specific test for the evaluation of testicular torsion. Early urology involvement is crucial to avoid testicular loss. The use of color flow is essential in .Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to .
testicular torsion vs epididymitis signs
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic .Testicular torsion is a painful twisting of a boy’s testicles and spermatic cord. Torsion causes blood to not flow to the testicles. . At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
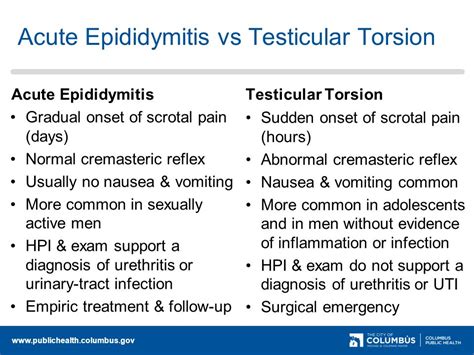
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies.
You might get one or more of these tests to diagnose testicular torsion: Urine test (checks for an infection) An imaging test of your scrotum, usually an ultrasound that uses sound waves to check .
Testicular torsion is a very serious condition and is considered a medical emergency. Rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord can cause obstruction of the arterial blood flow to the testicle, as well as the venous blood outflow, which can ultimately lead to necrosis or death of the testicular tissue.American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices.
The cremasteric reflex is most commonly performed in the evaluation of acute scrotal pain and the assessment for testicular torsion that is commonly associated with an apparent loss of the reflex.[1][2][3] . The muscle's name is derived from a Greek word meaning “suspender.” In reality, the muscle has 2 parts, a lateral and medial .
If you are a male who experiences sudden and severe pain in your belly, groin or testicle, Bruce Schlomer, M.D., Pediatric Urologist at Children's Health℠ and Associate Professor at UT Southwestern, has an important message for you: "Don't try to tough it out!" These may be signs of testicular torsion – a relatively common medical condition that requires immediate . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity. The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. .↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord .
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility. . Laboratory tests are unlikely to be of consequence, as no single test .Testicular torsion is an emergency condition. It happens when the spermatic cord, which provides blood flow to the testicle, rotates and becomes twisted. The twisting cuts off the testicle's blood supply and causes sudden pain and swelling. Testicular torsion requires surgery right away to save the .
moisture meter for plastic resin
Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips and sessions of hemocoagulation) required orchidectomy and . Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. . A healthcare professional may also test the patient’s cremasteric reflex, which is highly effective in helping diagnose .Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have . Definition: Twisting of the spermatic cord leading to decreased blood flow to the testicle resulting in ischemia, infarction and potentially, tissue necrosis. Epidemiology: Most common cause of acute scrotal pain in prepubertal boys; Torsion present in 3.2% of all children presenting to the ED with scrotal pain (Ben-Israel 2010) Bimodal frequency: peaks in 1st year .

Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.What is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion happens when one of your testicles twists around. Each testicle is attached to a spermatic cord, which contains blood vessels that carry blood to the testicle. In testicular torsion, this becomes twisted (called torsion) and blocks the flow of blood to the testicle. Testicular torsion is an emergency.
testicular torsion survival rate
testicular torsion signs on examination
A 25-year-old male is brought to the ED by EMS after sudden onset right testicular pain. He denies any trauma or contact to his scrotum or perineum; however, he endorses severe, sudden pain associated with nausea and non-bloody, non-bilious emesis. He additionally complains of mild lower right abdominal tenderness. Review of systems is otherwise .How is testicular torsion diagnosed? Diagnosis entails a physical examination and a complete medical history. A prompt diagnosis is imperative because prolonged testicular torsion may cause irreversible damage to the testes. Other diagnostic tests may be done, but there is no test that diagnoses testicular torsion accurately all the time. How common is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age. Testicular torsion is characterized by sudden-onset unilateral testicular pain, which may radiate to the lower abdomen, with nausea and vomiting. Clinical findings include a high-riding. testis. with an absent . cremasteric reflex. Imaging with .
moisture meter for plastics
Depending on the circumstances, your doctor might do a testicular exam followed by a blood test, ultrasound or biopsy. Most changes in your testicles aren't caused by testicular cancer. A number of noncancerous conditions can cause changes in your testicles, such as a cyst, injury, infection, hernia and collection of fluid around the testicles . Confirm the patient’s name and date of birth. . Prehn’s test is used to differentiate testicular pain caused by acute epididymitis and testicular torsion. The test involves elevating the testes to assess the impact on testicular pain. A reduction in testicular pain is associated with epididymitis. Testicular torsion is a urological emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischaemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies.
Although testicular torsion is rare, it is an emergency. Sudden testicular pain demands an immediate trip to the emergency room. If treatment is delayed, the testicle can die.
testicular torsion prognosis
Wethrift exists to help shoppers save money when they shop online. We help millions of shoppers save money every month by helping them discover the latest discount, promos, and . Ver mais
testicular torsion test name|testicular torsion prognosis